Objectives:
1) To study about Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
2) To understand the operation theory of Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
Method:
1) By making research in the internet
An analog-to-digital converter (ADC) converts analog signals into digital signals without altering their essential content. The analog information is transmitted by modulating a continuous transmission. Besides that, it is also by amplifying the strength of the signal or varying its frequency in order to add or subtract data. The input to an analog-to-digital converter consists of a voltage which varies among a theoretically infinite number of values. The output of the ADC defined levels or states. The simplest digital signals only have two states and are called binary. Digital signals are transmitted in a more efficient way than analog signals because well-defined digital impulses are easier for an electronic circuit to distinguish than chaotic noise. The characteristic curve of an ideal 3-bit ADC. The analog input range usually is from 0 V to 5 V. The input signal can be divided by 8 (2^3=8) ranges, at each range all the analog values use the same binary code to represent and this binary code is corresponding with the mid-value. Therefore, during the processing converter, it consists of ± 1/2 least significant bit (LSB) quantization uncertainty or quantization error and also includes the previous converter that has analog error, then all of the errors comprise the error value of ADC. The number of bits of the converter need to increase so that it can reduce the quantization error. The more the number of bits, the more the number ofranges and the data signal will be more detail. This is because the ± 1/2 LSB becomes small. Thus, the quantization error will reduce. When the digital output changes LSB, the required input voltage value also changes and this is known as quantization value (Q). The methods of conversion for analog to digital converter are various, sampel and hold (S&H) circuit which is it will capture the inpus signal Vin to avoid normally can be divided as analog-to-digital (A/D) conversion methods. htere are digital-ramp ADC, successive approximation ADC, flash ADC and tracking ADC.
There are many types of ADC but there are three types of ADC that commonly used. There are:
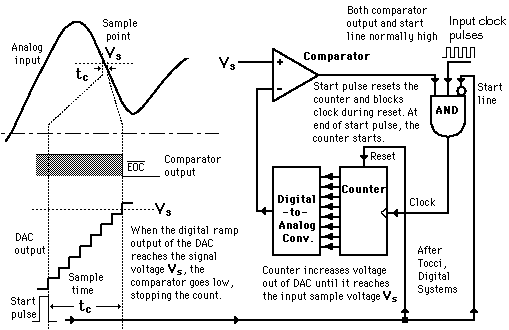
1) Digital Ramp ADC
The conversion from analog to digital form inherently involves comparator action whereby the value of the analog voltage at some point in time is compared with some standard. By applying the analog voltage to one terminal of a comparator and trigger a binary which drives a digital-to-analog converter (DAC), the value of the analog voltage at some point can get. The output of the DAC is applied to the other terminal of the comparator. Since the output of the DAC is increasing with the counter, it triggered the comparator at some point when its voltage exceeds the analog input. The transition of the comparator stops the binary counter which is at that point holds the digital value corresponding to the analog voltage.
Method:
1) By making research in the internet
An analog-to-digital converter (ADC) converts analog signals into digital signals without altering their essential content. The analog information is transmitted by modulating a continuous transmission. Besides that, it is also by amplifying the strength of the signal or varying its frequency in order to add or subtract data. The input to an analog-to-digital converter consists of a voltage which varies among a theoretically infinite number of values. The output of the ADC defined levels or states. The simplest digital signals only have two states and are called binary. Digital signals are transmitted in a more efficient way than analog signals because well-defined digital impulses are easier for an electronic circuit to distinguish than chaotic noise. The characteristic curve of an ideal 3-bit ADC. The analog input range usually is from 0 V to 5 V. The input signal can be divided by 8 (2^3=8) ranges, at each range all the analog values use the same binary code to represent and this binary code is corresponding with the mid-value. Therefore, during the processing converter, it consists of ± 1/2 least significant bit (LSB) quantization uncertainty or quantization error and also includes the previous converter that has analog error, then all of the errors comprise the error value of ADC. The number of bits of the converter need to increase so that it can reduce the quantization error. The more the number of bits, the more the number ofranges and the data signal will be more detail. This is because the ± 1/2 LSB becomes small. Thus, the quantization error will reduce. When the digital output changes LSB, the required input voltage value also changes and this is known as quantization value (Q). The methods of conversion for analog to digital converter are various, sampel and hold (S&H) circuit which is it will capture the inpus signal Vin to avoid normally can be divided as analog-to-digital (A/D) conversion methods. htere are digital-ramp ADC, successive approximation ADC, flash ADC and tracking ADC.
There are many types of ADC but there are three types of ADC that commonly used. There are:
1) Digital Ramp ADC
The conversion from analog to digital form inherently involves comparator action whereby the value of the analog voltage at some point in time is compared with some standard. By applying the analog voltage to one terminal of a comparator and trigger a binary which drives a digital-to-analog converter (DAC), the value of the analog voltage at some point can get. The output of the DAC is applied to the other terminal of the comparator. Since the output of the DAC is increasing with the counter, it triggered the comparator at some point when its voltage exceeds the analog input. The transition of the comparator stops the binary counter which is at that point holds the digital value corresponding to the analog voltage.
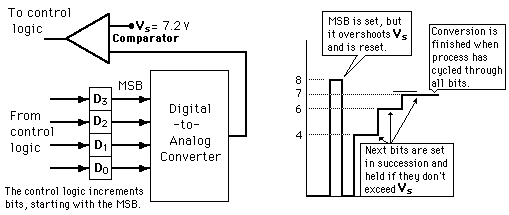
2) Successive Approximation ADC
This type of ADC is much faster than the digital ramp ADC because it uses digital logic to converge on the value closest to the input voltage. A comparator and a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) are used in the process. These is an illustration of 4-bit SAC with 1 volt step size.

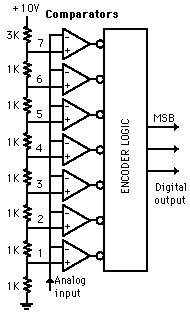
3) Flash ADC
A 3-bit flash ADC with resolution 1 volt is illustrated. The resistor net and comparators provide an input to the combinational logic circuit. Therefore, the conversion time is just the propagation delay through the network. Itis not limited by the clock rate or some convergence sequence. This type of ADC requires a comparator for each value of output although it is the fastest type of ADC. The ADCs are available in IC form up to 8-bit and 10-bit flash ADCs. A truth table has been executed from the encoder logic and then it is converted to the ladder of inputs to the binary number output.
Conclusion:
This week I am going to tell about the analog-to-digital converter (ADC) which is one of the important components to implement this project. This week I learned the type of ADC in industries and how this ADC will help me to do this project.
This week I am going to tell about the analog-to-digital converter (ADC) which is one of the important components to implement this project. This week I learned the type of ADC in industries and how this ADC will help me to do this project.
BetMGM Bonus Codes - GoOmans
ReplyDeleteClaim BetMGM casino 스포츠 분석 사이트 bonuses and promotions. Best BetMGM casino bonuses for 2021! Play slots and table games at one of 토토 먹튀 사례 the nextbet top-rated 안전 사설 토토 사이트 online 프로즌 먹튀 casinos,